Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的人是患丙型肝炎的高危人。
Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的人是患丙型肝炎的高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在丙肝感染者中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响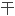
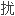 素的疗效。
素的疗效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性丙肝 人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫
人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和糖尿 是慢性丙型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
是慢性丙型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗 毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并肝硬化的慢性丙肝(CHC)患者接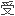 α
α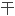
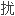 素包括派罗欣治疗时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
素包括派罗欣治疗时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。

 肝炎;C
肝炎;C 肝炎
肝炎Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的人是

 肝炎的高危人。
肝炎的高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在 肝感染者中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
肝感染者中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性 肝
肝 人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫
人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和糖尿 是慢性
是慢性
 肝炎(CHC)中
肝炎(CHC)中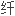
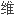
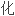 进展以及对抗
进展以及对抗 毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并肝硬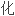 的慢性
的慢性 肝(CHC)
肝(CHC) 者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
 型肝炎;C型肝炎
型肝炎;C型肝炎Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的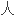
 患
患 型肝炎的高危
型肝炎的高危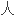 。
。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.

 肝感染者中,重叠感染隐匿
肝感染者中,重叠感染隐匿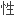 HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,
 肝
肝
 ,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫
,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和糖尿


 型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗 毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并肝硬化的
 肝(CHC)患者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存
肝(CHC)患者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存 肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词 分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过
分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过 工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的人是患丙型肝炎的高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在丙肝感染者中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰 的疗效。
的疗效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性丙肝 人,TH1细胞活
人,TH1细胞活 表达显著并与肝免疫
表达显著并与肝免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛 抵抗和糖尿
抵抗和糖尿 是慢性丙型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
是慢性丙型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗 毒治疗无应答的危险
毒治疗无应答的危险
 。
。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
 并肝硬化的慢性丙肝(CHC)患者接受α干扰
并肝硬化的慢性丙肝(CHC)患者接受α干扰 包括派罗欣治疗时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
包括派罗欣治疗时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
 炎;C型
炎;C型 炎
炎Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品 人是患丙型
人是患丙型 炎
炎 高危人。
高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在丙 感染者中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素
感染者中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素
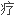
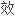 。
。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性丙
 人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并
人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并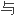

 疫
疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和糖尿 是慢性丙型
是慢性丙型 炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗 毒治
毒治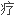 无应答
无应答 危险因素。
危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并 硬化
硬化 慢性丙
慢性丙 (CHC)患者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治
(CHC)患者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治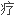 时存在
时存在 功能失代偿和死亡风险。
功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件 观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
 炎;C型
炎;C型 炎
炎Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的人是患丙型 炎的高危人。
炎的高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在丙

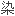 者中,重叠
者中,重叠
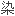 隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性丙
 人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与
人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与 免疫
免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和
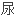
 是慢性丙型
是慢性丙型 炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗 毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并 硬化的慢性丙
硬化的慢性丙 (CHC)患者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在
(CHC)患者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在 功能失代偿和死亡风险。
功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.

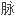 注射
注射 品的人是患丙型肝炎的高危人。
品的人是患丙型肝炎的高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在丙肝感染者中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的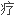 效。
效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性丙肝 人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫
人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与肝免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和糖尿 是慢性丙型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
是慢性丙型肝炎(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗

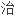
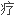 无应答的危险因素。
无应答的危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并肝硬化的慢性丙肝(CHC)患者接受α干扰素包括派罗欣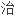
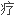 时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
时存在肝功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。


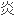 ;C
;C

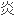
Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的人是 丙
丙

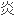 的高危人。
的高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在丙 感染
感染 中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性丙
 人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与
人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与 免疫
免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和糖尿 是慢性丙
是慢性丙

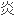 (CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗 毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并 硬化的慢性丙
硬化的慢性丙 (CHC)
(CHC)
 接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在
接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在 功能失代偿和死亡风险。
功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。


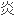 ;C
;C

Intravenous drug users are in a high-risk category for hepatitis C.
静脉注射毒品的人是 丙
丙

 的高危人。
的高危人。
In hepatitis C patients, occult HBV coinfection will reduce the response to interferon.
在丙 感染
感染 中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
中,重叠感染隐匿性HBV会影响干扰素的疗效。
Our findings show that in chronic hepatitis C, TH1 cytokines predominate and correlate to liver immunopathology.
研究结果显示,慢性丙
 人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与
人,TH1细胞活素表达显著并与 免疫
免疫 理机制相关。
理机制相关。
Moreover presence of insulin resistance and diabetes are risk factors for fibrosis progression and nonresponse to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
此外,胰岛素抵抗和糖尿 是慢性丙
是慢性丙

 (CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗
(CHC)中纤维化进展以及对抗 毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
毒治疗无应答的危险因素。
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGASYS.
合并 硬化的慢性丙
硬化的慢性丙 (CHC)
(CHC)
 接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在
接受α干扰素包括派罗欣治疗时存在 功能失代偿和死亡风险。
功能失代偿和死亡风险。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。